
NGS- und PCR-Cleanup .
Magnetic Beads sind sehr effizient bei der Aufreinigung von PCR-Produkten und der Größenselektion von Amplikons bei der Sequenzierung.
Unsere MagSi-NGSPREP Plus Beads können direkt in bereits etablierten NGS-Protokollen genutzt werden, z.B. anstelle von Ampure XP Beads.
Mit den MagSi-DT Removal Beads lassen sich Dye-Terminatoren und nicht inkorporierte Farbstoffe aus Sequenzierungsreaktionen entfernen – ohne Zentrifugation oder Filtration .
Hard Facts .
- Kompatibel mit existierenden Protokollen
- Hohe Reinheit und Recovery
- Einfach skalierbar und HTS-kompatibel
- MagSi DT-Removal: Entfernung von Verunreinigungen wie Dye-Terminatoren
- MagSi-NGSPREPplus: SPRI-basierte Size-Selection
- Garantieren konsistente und robuste Ergebnisse

Anwendungen .
Die library preparation ist einer der wichtigsten Schritte in der Probenvorbereitung für NGS Reaktionen. MagSi NGS Beads ermöglichen eine einfache Größenselektion durch die Variation des Bead : Probe-Verhältnisses.
Die MagSi-NGSPREP Plus Beads sind auch geeignet für eine Größenselelektion Ihrer PCR-Produkte (SPRI).
Durch Variation des Beads:Sample-Verhältnisses können Sie gezielt erwünschte Fragmentgrößen selektieren bzw. unerwünschte Fragmentgrößen entfernen.
Mit den MagSi-NGSPREP Plus Beads entfernen Sie Enzyme, Primer, Oligonukleotide, sowie Polymerasen und Salze einfach und schnell aus Ihrem PCR-Produkt.
Entfernen von nicht inkorporierten Farbstoffen und Salzen nach Sequenzierungs-Reaktionen mit unseren MagSi-DT Removal Beads.
Mit einem angepassten Protokoll können die MagSi-NGSPREP Plus Beads auch zur Anreicherung von RNA verwendet werden, um die Sensitiviät und Spezifität der Reversen Transription und qPCR-Analyse zu verbessern.
Simon, B., Pichon, M., Valette, M., Burfin, G., Richard, M., Lina, B., & Josset, L. (2019). Whole Genome Sequencing of A(H3N2) Influenza Viruses Reveals Variants Associated with Severity during the 2016–2017 Season. Viruses, 11(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020108
Details .
Easy-to-use .
- MagSi-NGSPREP: Ein Produkt für all Cleanup- und Größenselektions-Schritte im library preparation Workflow
- Unkompliziertes Protokoll mit Bind-Wasch-Elute-Verfahren
- Für manuelle und automatisierte Workflows
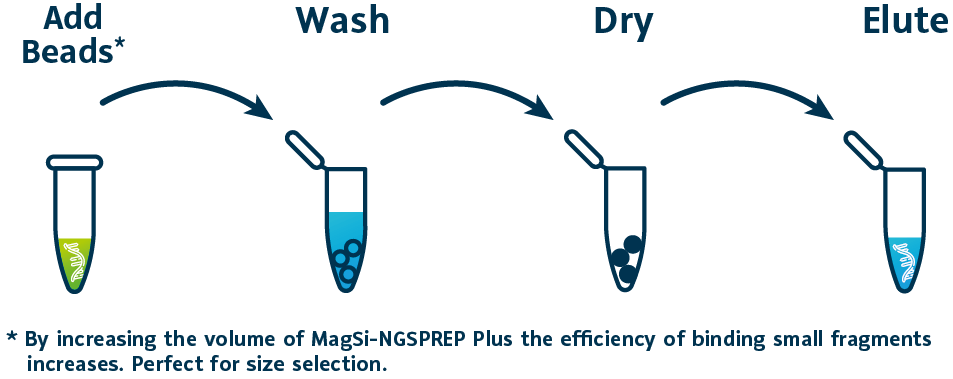
MagSi-NGSPREP Plus .
Unsere MagSi-NGSPREP Plus Beads sind sehr effizient bei NGS-Anwendungen, sowohl bei der Größenselektion als auch für das Clean-up der Library Prep.
- Hervorragende Aufreinigung von PCR-Produkten
- Effiziente Entfernung von Enzymen, Primern, Oligonukleotiden, Polymerasen und anderen Verunreinigungen
- Garantiert konsistente Sequenzierergebnisse
- Protokoll identisch mit Agencourt AMPure XP®
- Einfach zu automatisieren, geeignet für HTS
- Optimierte Protokolle für Liquid Handler verfügbar (Biomek®, Hamilton® Microlab STAR)
- Auch geeignet für Liquid Handler von PerkinElmer®, Agilent Technologies® u.a.
- Beste Performance in Kombination mit unseren Magnetplatten für 96- und 384-Well Platten
MagSi-NGSPREP Beads für beste Ergebnisse .
- Hohe Recovery
- Fragmentgrößenselektion einstellbar zwischen 100 und 1000 Basenpaaren
- Garantiert konsistente Sequenzierergebnisse
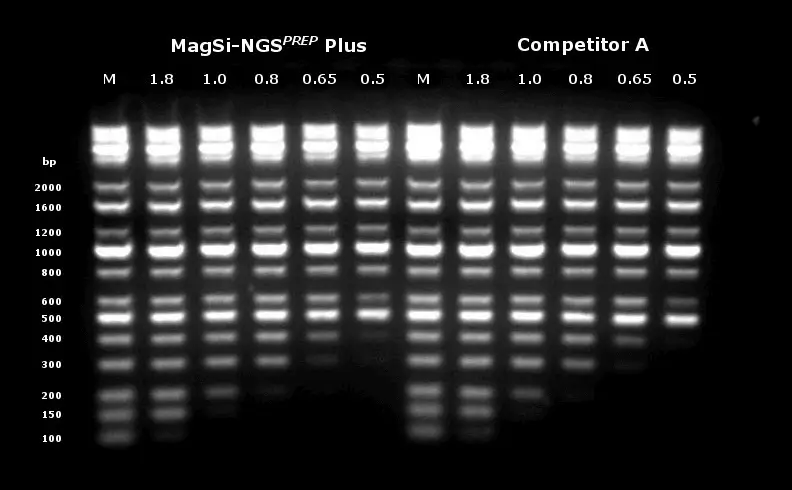
Größenselektion einer DNA-Ladder mittels unterschiedlicher Verhältnisse von Bead zu Probe (0.5x bis 1.8x). Oben auf Agarose-Gel, unten mit Bioanalyser-Messungen.
Quelle: magtivio
MagSi-DT Removal Beads .
MagSi-DT Removal Beads sind sehr effiziente bei der Entfernung von Dye-Terminatoren aus BigDye®-Sequenzierungsreaktionen.
- Hohe Signalintensität und Phred 20 Read-Länge
- Effiziente Entfernung von nicht eingebauten Dye-Terminatoren und Salzen
- Konsistente und robuste Performance
- Einfache Automatisierung, HTS-kompatibel
- Keine Zentrifugation oder Filtration nötig
- Direkte Aufreinigung der Reaktionen in den Reaktionsplatten
- Protokoll identisch mit Agencourt CleanSEQ®
- Optimiert für Biomek® Workstations und Hamilton® Microlab STARline
- Kompatibel mit vielen anderen automatisierten Liquid-Handling-Systemen (z.B. PerkinElmer®, Caliper Life Sciences®, etc.)
MagSi-DT Removal Beads für beste Ergebnisse .
Die MagSi-DT Removal Beads sind sehr effizient bei der Entfernung von Dye-Terminatoren aus BigDye®-Sequenzierungsreaktionen.
- Effiziente Beseitigung nicht inkorporierter Dye-Terminatoren und Salzen
- Hohe Signalintensitäten und lange Phred 20-Leselängen
- Hohe Pass-Rates
- Konsistente Performance

NGS- und DT Removal Beads .
Downloads .
Simon, B., Pichon, M., Valette, M., Burfin, G., Richard, M., Lina, B., & Josset, L. (2019). Whole Genome Sequencing of A(H3N2) Influenza Viruses Reveals Variants Associated with Severity during the 2016–2017 Season. Viruses, 11(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020108
Recovery of Methanotrophic Activity Is Not Reflected in the Methane-Driven Interaction Network after Peat Mining | Applied and Environmental Microbiology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Multi‐omics integration identifies a selective vulnerability of colorectal cancer subtypes to YM155 – Zhan – 2021 – International Journal of Cancer – Wiley Online Library. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Microeukaryotic Communities on the Fruit of Gardenia thunbergia Thunb. with a Focus on Pathogenic Fungi. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
When the going gets tough: Emergence of a complex methane-driven interaction network during recovery from desiccation-rewetting – ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Association between childhood maltreatment, psychopathology and DNA methylation of genes involved in stress regulation: Evidence from a study in Borderline Personality Disorder. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Impact of PNPase on the transcriptome of Rhodobacter sphaeroides and its cooperation with RNase III and RNase E | SpringerLink. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Ammonium Removal in Aquaponics Indicates Participation of Comammox Nitrospira | SpringerLink. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Active metabolic pathways of anaerobic methane oxidation in paddy soils – ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Limited antimicrobial efficacy of oral care antiseptics in microcosm biofilms and phenotypic adaptation of bacteria upon repeated exposure | SpringerLink. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Monitoring and contamination incidence of gnotobiotic experiments performed in microisolator cages – ScienceDirect. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Communities in Agricultural Soils from Vietnam with Special Attention to Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Forests | Free Full-Text | Impact of Soil-Applied Microbial Inoculant and Fertilizer on Fungal and Bacterial Communities in the Rhizosphere of Robinia sp. and Populus sp. Plantations. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Induced systemic resistance impacts the phyllosphere microbiome through plant-microbe-microbe interactions | bioRxiv. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Allergies | Free Full-Text | Could Modifying the Skin Microbiome, Diet, and Lifestyle Help with the Adverse Skin Effects after Stopping Long-Term Topical Steroid Use? (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Structure-based analyses of Salmonella RcsB variants unravel new features of the Rcs regulon | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford Academic. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Life | Free Full-Text | The Effect of a Total Fishmeal Replacement by Arthrospira platensis on the Microbiome of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus). (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Densely Populated Water Droplets in Heavy-Oil Seeps | Applied and Environmental Microbiology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Early Stage Root-Associated Fungi Show a High Temporal Turnover, but Are Independent of Beech Progeny. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Pulmonary microbiome patterns correlate with the course of disease in patients with sepsis-induced ARDS following major abdominal surgery – Journal of Hospital Infection. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Frontiers | Novel Antimicrobial Cellulose Fleece Inhibits Growth of Human-Derived Biofilm-Forming Staphylococci During the SIRIUS19 Simulated Space Mission | Microbiology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Staphylococcus saccharolyticus: An Overlooked Human Skin Colonizer. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Frontiers | Targeted De-Methylation of the FOXP3-TSDR Is Sufficient to Induce Physiological FOXP3 Expression but Not a Functional Treg Phenotype | Immunology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
PD-1 (PDCD1) promoter methylation in Merkel cell carcinoma: prognostic relevance and relationship with clinico-pathological parameters | Modern Pathology. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Targeted bisulfite sequencing: A novel tool for the assessment of DNA methylation with high sensitivity and increased coverage – PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Transcriptional mutagenesis dramatically alters genome-wide p53 transactivation landscape – PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Global discovery of bacterial RNA-binding proteins by RNase-sensitive gradient profiles reports a new FinO domain protein – PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
BG – Authigenic formation of Ca–Mg carbonates in the shallow alkaline Lake Neusiedl, Austria. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
An RNA-centric global view of Clostridioides difficile reveals broad activity of Hfq in a clinically important Gram-positive bacterium | bioRxiv. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Prevalence of p53 dysregulations in feline oral squamous cell carcinoma and non-neoplastic oral mucosa – PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Land Use Change and Water Quality Use for Irrigation Alters Drylands Soil Fungal Community in the Mezquital Valley, Mexico – PubMed. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022

