
Functionalized beads .
The MagSi-Tools product line provides surface-activated magnetic beads. Different surface modifications and bead sizes are available for applications such as immobilization of proteins, purification of nucleic acids or coupling of a wide variety of molecules.
Hard Facts .
- Different surface modifications
- Coupling of proteins, peptides, antibodies, nucleic acids
- Simple coupling protocol
- Various bead sizes available
- Easily automated

Applications .
MagSi-S COOH beads with carboxyl surface are suitable for the preconcentration of metals in liquid samples. For analysis, the metals can be detached from the beads again by electrophoretic buffers.
Carpio, A., Mercader-Trejo, F., Arce, L., & Valcárcel, M. (2012). Use of carboxylic group functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for the preconcentration of metals in juice samples prior to the determination by capillary electrophoresis: CE and CEC. ELECTROPHORESIS, 33(15), 2446-2453. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201100636
Lectins can be covalently coupled to MagSi-S Tosyl 1.0 beads to purify glycoproteins.
Engel, N. Y., Weiss, V. U., Wenz, C., Glück, S., Rüfer, A., Kratzmeier, M., Marchetti-Deschmann, M., & Allmaier, G. (2017). Microchip capillary gel electrophoresis combined with lectin affinity enrichment employing magnetic beads for glycoprotein analysis. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(28), 6625-6634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0615-0
Enzymes can also be immobilized on magnetic beads, e.g. for studies of kinetics or function experiments.
Huang, S., Celá, A., Adams, E., Glatz, Z., & Van Schepdael, A. (2020). Aldehyde oxidase assay by capillary electrophoresis: From off-line, online up to immobilized enzyme reactor. Journal of Separation Science, 43(17), 3565-3572. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202000412
Oligonucleotides can be covalently bound to the beads (e.g. MagSi-S NH2, MagSi-S CHO) for capture assays or specific enrichment of targets.
Magnetic beads are also perfect for diagnostic purposes. They are often used for the detection of viruses, specific proteins, or cells.
Details of the MagSi-S Tools Beads .
Overview of functional surfaces .
| MagSi-S bead | Surface | Structure | Target molecule | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MagSi-S (Silica) | – | R-OH | Individual functionalization | |
| MagSi-S CHO (Aldehyd) | Aldehyde | R-CHO | NH2 (amine) | Protein immobilization |
| MagSi-S COOH (Carboxyl) | Carboxyl | R-COOH | NH2 (amine); lysine, cysteine, histidine, tyrosine | Immobilization of peptides, proteins, antibodies |
| MagSi-S Epoxy | Epoxy |  | NH2 (amine); lysine, cysteine, histidine, tyrosine | Immobilization of enzymes, peptides and proteins |
| MagSi-S Hydrazide | Hydrazide | R-CO-N2H2 | Oligosaccharide groups | Immobilization of antibodies, peptides, proteins and glycoproteins |
| MagSi-S NH2 (Amin) | NH2 | R-NH2 | Amine, aldehyde | Protein immobilization |
| MagSi-S SH (Sulfydryl) | SH | R-SH | Free cysteine | Immobilization of molecules via cysteine groups and immobilization on gold surfaces |
| MagSi-S Tosyl | Tosyl | 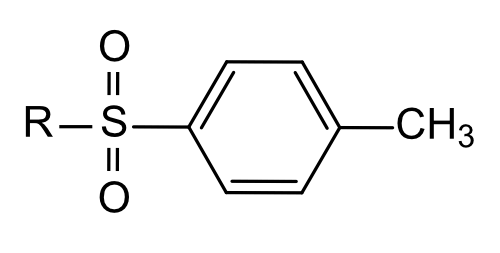 | SH (Sulfhydryl) and NH2 (amine) | Immobilization of antibodies, peptides and proteins |
Coupling chemistries of different beads .
| Bead surface | Needed chemicals | Protein binding | Treatment | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carboxyl [1] (COOH) | EDC / NHS | Amine groups (of lysine and/or as unblocked N-termini) lysine, histidine, cysteine, tyrosine, etc. | No treatment necessary | Can be used for coupling for most proteins |
| Aldehyde (CHO) | Aldehyd/Amin reaction | Amine groups | No treatment necessary | Add reducing agent to stabilize the amide bond |
| Thiol (SH) | Redox reaction [3] | Free cysteine | Reduction of disulfides under non-denaturing conditions to generate free cysteine | Useful for cysteine-containing proteins. Multiple coupling possible |
| Amine [2] (NH2) | Gluteraldehyde | Amine/Aldehyde | No treatment necessary | Add reducing agent to stabilize the amide bond |
| Tosyl | None | Sulfhydryl, amine groups | No treatment necessary | Useful for antibodies |
| Hydrazide | Sodium perodiate | Oligosaccharide groups | Oxidation of glycoproteins under non-denaturing conditions | Useful for glycoproteins |
| Epoxy | Adsorption / reaction support | Lysine, histidine, cysteine, tyrosine, etc. | No treatment necessary | Useful for enzymes |
[2] Gluteraldehyd führt zu einer stabileren Proteinbindung als die Carbodiimid-Reagenzien, die mit Carboxylat-Beads verwendet werden.
[3] Reduktion der Disulfide mit 0,1 M DTE (Dithioerythrol); Kopplung des Proteins bei einem pH-Wert unterhalb des isoelektrischen Punkts; Deaktivierung des überschüssigen Thiols mit 20 mM PDEA (2-(2-Pyridinyldithio)ethan-Amin)/ 1M NaCl, pH 4,3
Abkürzungen: EDC, N-Ethyl-N’-(dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimid; NHS, N-Hydroxysuccinimid.
Technical data .
| MagSi-S Tools 600 | MagSi-S Tools 1.0 | MagSi-S Tools 3.0 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | 600 nm | 1.0 µm | 3.0 µm |
| Concentration | 10 mg/ml | ||
| Beads/ml | 8 – 20 * 10^9 | 6 – 12 * 10^9 | 1 – 3 * 10^9 |
| Product volume | 2 ml, 10 ml, 100 ml | ||
| Material | Magentic silica beads with activated surface | ||
| Magnetic content | 40% | 60% | 60% |
| Size distribution (D5 – D95) | 500 – 900 nm | 0,7 – 1,4 µm | 0,6 – 10,0 µm |
| Buffer solution | MagSi-Tools, surface activated: PBS (pH 7.4), 0.05% sodium azide (NaN3, Toxic!), except: 1) MagSi-S, unmodified silica beads and MagSi-S NH2, amine-modified silica beads: Water, 0.05% sodium azide. 2) Epoxy and tosyl activated beads are supplied in DSMO:THF 1:1. | ||
| Storage | at 2 – 8°C |
MagSi-S Beads .
Magnetic silica particles for proprietary development.
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD16003 | 2 ml | MagSi-S 600 | 10 mg/mL | 600 nm |
| MD18003 | 10 ml | |||
| MD19003 | 100 ml | |||
| MD01003 | 2 ml | MagSi-S 1.0 | 10 mg/mL | 1.0 µm |
| MD03003 | 10 ml | |||
| MD04003 | 100 ml | |||
| MD41003 | 2 ml | MagSi-S 3.0 | 10 mg/mL | 3.0 µm |
| MD43003 | 10 ml | |||
| MD44003 | 100 ml |
MagSi-S COOH Beads .
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD16004 | 2 mL | MagSi-S COOH 600 | 10 mg/mL | 600 nm |
| MD18004 | 10 mL | |||
| MD19004 | 100 mL | |||
| MD01004 | 2 mL | MagSi-S COOH 1.0 | 10 mg/mL | 1.0 µm |
| MD03004 | 10 mL | |||
| MD04004 | 100 mL | |||
| MD41004 | 2 mL | MagSi-S COOH 3.0 | 10 mg/mL | 3.0 µm |
| MD43004 | 10 mL | |||
| MD44004 | 100 mL |
MagSi-S Tosyl Beads .
Magnetic silica particles with tosyl modified surface. Intended for tosyl coupling chemistry with antibodies and proteins.
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD16008 | 2 mL | MagSi-S Tosyl 600 | 10 mg/mL | 600 nm |
| MD18008 | 10 mL | |||
| MD19008 | 100 mL | |||
| MD01008 | 2 mL | MagSi-S Tosyl 1.0 | 10 mg/mL | 1.0 µm |
| MD03008 | 10 mL | |||
| MD04008 | 100 mL | |||
| MD41008 | 2 mL | MagSi-S Tosyl 3.0 | 10 mg/mL | 3.0 µm |
| MD43008 | 10 mL | |||
| MD44008 | 100 mL |
MagSi-S NH2 Beads .
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD16005 | 2 ml | MagSi-S NH2 600 | 10 mg/mL | 600 nm |
| MD18005 | 10 ml | |||
| MD19005 | 100 ml | |||
| MD01005 | 2 ml | MagSi-S NH2 1.0 | 10 mg/mL | 1.0 µm |
| MD03005 | 10 ml | |||
| MD04005 | 100 ml | |||
| MD41005 | 2 ml | MagSi-S NH2 3.0 | 10 mg/mL | 3.0 µm |
| MD43005 | 10 ml | |||
| MD44005 | 100 ml |
MagSi-S SH Beads .
Magnetic silica particles with modified surface for SH coupling chemistry.
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD18006 | 10 ml | MagSi-S SH 600 | 10 mg/ml | 600 nm |
| MD19006 | 100 ml | |||
| MD03006 | 10 ml | MagSi-S SH 1.0 | 10 mg/ml | 1.0 µm |
| MD04006 | 100 ml | |||
| MD43006 | 10 ml | MagSi-S SH 3.0 | 10 mg/ml | 3.0 µm |
| MD44006 | 100 ml |
MagSi-S CHO Beads .
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD18007 | 10 ml | MagSi-S CHO 600 | 10 mg/ml | 600 nm |
| MD19007 | 100 ml | |||
| MD03007 | 10 ml | MagSi-S CHO 1.0 | 10 mg/ml | 1.0 µm |
| MD04007 | 100 ml | |||
| MD43007 | 10 ml | MagSi-S CHO 3.0 | 10 mg/ml | 3.0 µm |
| MD44007 | 100 ml |
MagSi-S Hydrazide Beads .
Magnetic silica particles with hydrazide modified surface. Intended for immobilization of antibodies, glycoproteins or other aldehyde containing molecules.
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD16013 | 2 ml | MagSi-S Hydrazide 600 | 10 mg/ml | 600 nm |
| MD18013 | 10 ml | |||
| MD19013 | 100 ml | |||
| MD01013 | 2 ml | MagSi-S Hydrazide 1.0 | 10 mg/ml | 1.0 µm |
| MD03013 | 10 ml | |||
| MD04013 | 100 ml | |||
| MD41013 | 2 ml | MagSi-S Hydrazide 3.0 | 10 mg/ml | 3.0 µm |
| MD43013 | 10 ml | |||
| MD44013 | 100 ml |
MagSi-S Epoxy Beads .
Magnetic silica particles with epoxy modified surface. Intended for coupling to enzymes and other NH2-containing molecules.
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD16010 | 2 ml | MagSi-S Epoxy 600 | 10 mg/ml | 600 nm |
| MD18010 | 10 ml | |||
| MD19010 | 100 ml | |||
| MD01010 | 2 ml | MagSi-S Epoxy 1.0 | 10 mg/ml | 1.0 µm |
| MD03010 | 10 ml | |||
| MD04010 | 100 ml | |||
| MD41010 | 2 ml | MagSi-S Epoxy 3.0 | 10 mg/ml | 3.0 µm |
| MD43010 | 10 ml | |||
| MD44010 | 100 ml |
MagSi-S functional beads .
Downloads .
Carpio, A., Mercader-Trejo, F., Arce, L., & Valcárcel, M. (2012). Use of carboxylic group functionalized magnetic nanoparticles for the preconcentration of metals in juice samples prior to the determination by capillary electrophoresis: CE and CEC. ELECTROPHORESIS, 33(15), 2446-2453. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201100636
Engel, N. Y., Weiss, V. U., Wenz, C., Glück, S., Rüfer, A., Kratzmeier, M., Marchetti-Deschmann, M., & Allmaier, G. (2017). Microchip capillary gel electrophoresis combined with lectin affinity enrichment employing magnetic beads for glycoprotein analysis. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 409(28), 6625-6634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0615-0
Huang, S., Celá, A., Adams, E., Glatz, Z., & Van Schepdael, A. (2020). Aldehyde oxidase assay by capillary electrophoresis: From off-line, online up to immobilized enzyme reactor. Journal of Separation Science, 43(17), 3565-3572. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.202000412

