

qPCR with SYBR® Green .
Our new primaQUANT CYBR ADVANCED qPCR Master Mix with SYBR® Green was developed from scratch and shines in all essential performance criteria. Its high sensitivity (detection limit 1 template), wide dynamic range and high robustness guarantee reproducible results, even under difficult conditions. It is therefore the perfect choice for qPCR with SYBR®Green
The primaQUANT CYBR ADVANCED qPCR Master Mix with SYBR® Green is very temperature-stable. It does not need to be pipetted onto ice and the Master Mix can be stored at room temperature for several days or in the refrigerator for several weeks without any problems.
The primaQUANT CYBR ADVANCED qPCR Master Mix with SYBR® Green replaces the primaQUANT CYBR Master Mixes with the article numbers SL-9902, SL-9902R, SL-9902HR, SL-9902B, SL-9902RB, SL-9902HRB.
Hard Facts .
- Excellent sensitivity: 1 template per reaction
- Ultra-Fast: qPCR in 15 minutes
- Hot-start polymerase
- Stable at room temperature - pipetting without ice
- Suitable for melting curve analysis
- Full control: Optionally with blue dye
- Developed & manufactured in Germany

Applications .
With the primaQUANT CYBR qPCR Master Mix, you can perform genotyping using High-Resolution Melting Curves (HRM) – without the need for agarose gels.
Li, W., Matsuoka, M., Kai, M., Thapa, P., Khadge, S., Hagge, D. A., Brennan, P. J., & Vissa, V. (2012). Real-Time PCR and High-Resolution Melt Analysis for Rapid Detection of Mycobacterium leprae Drug Resistance Mutations and Strain Types. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 50(3), 742-753. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.05183-11
Słomka, M., Sobalska-Kwapis, M., Wachulec, M., Bartosz, G., & Strapagiel, D. (2017). High Resolution Melting (HRM) for High-Throughput Genotyping-Limitations and Caveats in Practical Case Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112316
Lefever, S., Rihani, A., Van der Meulen, J., Pattyn, F., Van Maerken, T., Van Dorpe, J., Hellemans, J., & Vandesompele, J. (2019). Cost-effective and robust genotyping using double-mismatch allele-specific quantitative PCR. Scientific Reports, 9(1), 2150. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38581-z
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping is widely used in genetic studies to determine the factors underlying inherited traits.
Baris, I., Etlik, O., Koksal, V., Ocak, Z., & Baris, S. T. (2013). SYBR green dye-based probe-free SNP genotyping: introduction of T-Plex real-time PCR assay. Analytical Biochemistry, 441(2), 225-231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2013.07.007
Dhas, D. B. B., Ashmi, A. H., Bhat, B. V., Parija, S. C., & Banupriya, N. (2015). Modified low cost SNP genotyping technique using cycle threshold (Ct) & melting temperature (Tm) values in allele specific real-time PCR. The Indian Journal of Medical Research, 142(5), 555-562. https://doi.org/10.4103/0971-5916.171282
Pang, Y., Zhou, Y., Wang, S., Lu, J., Lu, B., He, G., Wang, L., & Zhao, Y. (2011). A novel method based on high resolution melting (HRM) analysis for MIRU-VNTR genotyping of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Journal of Microbiological Methods, 86(3), 291-297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2011.05.016
Bai, L., Deng, Y.-M., Dodds, A. J., Milliken, S., Moore, J., & Ma, D. D. F. (2006). A SYBR green-based real-time PCR method for detection of haemopoietic chimerism in allogeneic haemopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. European Journal of Haematology, 77(5), 425-431. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0609.2006.00729.x
Weksberg, R., Hughes, S., Moldovan, L., Bassett, A. S., Chow, E. W., & Squire, J. A. (2005). A method for accurate detection of genomic microdeletions using real-time quantitative PCR. BMC Genomics, 6, 180. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-6-180
To determine the expression of a gene (gene or RNA expression), the total RNA must first be transcribed into cDNA.
For separate cDNA synthesis, our primaREVERSE RT Kit is the first choice.
Alternatively, you can also use our primaQUANT 1STEP One-Step RT-qPCR Kit and directly use RNA in a qPCR.
The length of telomeres is well suited as a biomarker for cell aging. This also allows studying the impact of environmental influences on cell aging processes. qPCR is a rapid, reliable, and inexpensive method to study telomere lengths.
Lin, J., Smith, D. L., Esteves, K., & Drury, S. (2019). Telomere length measurement by qPCR – Summary of critical factors and recommendations for assay design. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 99, 271-278. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.10.005
More information:
High Resultion Melting Curve Analysis (HRM) makes it easy to detect the smallest changes in the genome, such as SNPs and mutations, using qPCR.
Matsuda, K. (2017). PCR-Based Detection Methods for Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism or Mutation: Real-Time PCR and Its Substantial Contribution Toward Technological Refinement. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, 80, 45-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.acc.2016.11.002
Simko, I. (2016). High-Resolution DNA Melting Analysis in Plant Research. Trends in Plant Science, 21(6), 528-537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.01.004
Mohammad Rahimi, H., Pourhosseingholi, M. A., Yadegar, A., Mirjalali, H., & Zali, M. R. (2019). High-resolution melt curve analysis: A real-time based multipurpose approach for diagnosis and epidemiological investigations of parasitic infections. Comparative Immunology, Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, 67, 101364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cimid.2019.101364
Next-generation sequencing requires accurate quantification of the DNA library to be sequenced for optimal results and high yields.
Such DNA libraries can be quantified inexpensively, rapidly and accurately by qPCR. By avoiding unnecessarily long PCR amplifications, the NGS workflow can be optimized, and amplification biases are also minimized.
Buehler, B., Hogrefe, H. H., Scott, G., Ravi, H., Pabón-Peña, C., O’Brien, S., Formosa, R., & Happe, S. (2010). Rapid quantification of DNA libraries for next-generation sequencing. Methods (San Diego, Calif.), 50(4), p15-18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.01.004
Copy number variants can be measured by SYBR-Green qPCR using different Cq values after a calibration. In addition, the melting curve information allows an estimation of whether there are SNPs within the CNVs.
Loewe, R. P. (2013). Combinational usage of next generation sequencing and qPCR for the analysis of tumor samples. Methods (San Diego, Calif.), 59(1), 126-131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2012.11.002
Diagnosis of pathogens can also be performed by nucleic acid analysis.
DNA pathogens (DNA viruses, bacteria, fungi) can be analyzed directly by quantitative PCR. For RNA pathogens (RNA viruses, e.g. SARS-COV2), a transcription of RNA into cDNA is necessary. For this purpose, we offer the primaREVERSE RT cDNA synthesis kit. Alternatively, you can perform cDNA synthesis and qPCR in one step with our primaQUANT 1-STEP Master Mixes.
Due to the particularly high purity of our primaQUANT Master Mixes, they can be used for quality control, e.g. to exclude the possibility that a product is contaminated with nucleic acids or nucleases.
Features .
Excellent performance .
The primaQUANT ADVANCED qPCR Master Mixes with SYBR Green offer a wide dynamic range and excellent performance, even with low template quantities or targets with low expression.
- Early cq values
- Wide Dynamic Range
- Low variance within replicates
- Limit-of-detection of 1 template per reaction
- Detection limit for cDNA of 0.1 pg per reaction
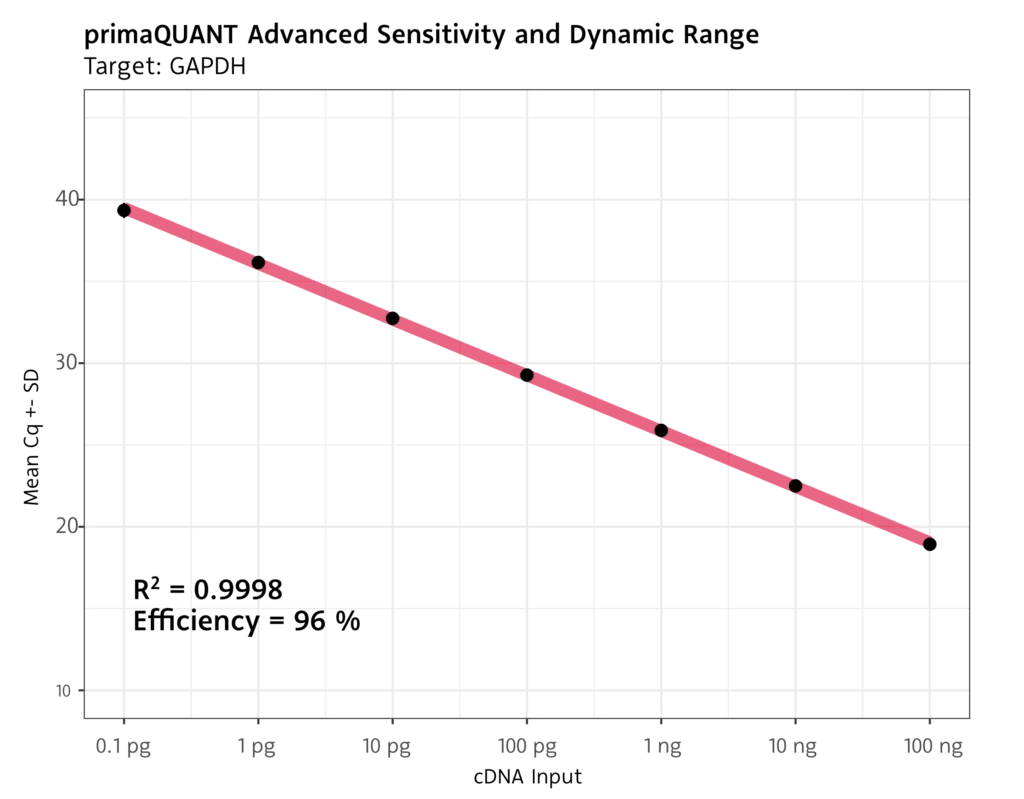
Robust quantification even at low Cq values at the detection limit.
Wide Dynamic Range with excellent efficiency.
No template inhibition for large amounts of input
For all qPCR cyclers .
Our qPCR 2x Master Mixes are suitable for all common qPCR cyclers and optionally available with ROX.
We have compiled a table for you showing whether your device uses ROX(6-carboxy- X-rhodamine) for normalization and which concentration, if any, is required.
| Manufacturer | qPCR cycler | ROX necessary? |
|---|---|---|
| Applied Biosystems / Thermo Fischer | StepOne™ Real-Time PCR System | high ROX |
| StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR System | high ROX | |
| 7500 Real-Time PCR System | low ROX | |
| 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System | low ROX | |
| 7500 Fast Dx Real-Time PCR Instrument | low ROX | |
| 7500 Real-Time PCR System for Human Identification | low ROX | |
| 7300 Real-Time PCR System | high ROX | |
| Viia™ 7 Real-Time PCR System | low ROX | |
| 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System | high ROX | |
| OpenArray® Real-Time PCR Platform | high ROX | |
| PRISM® 7000 Sequencing Detection System | high ROX | |
| PRISM® 7700 Sequencing Detection System | high ROX | |
| PRISM® 7900 Sequencing Detection System | high ROX | |
| Gene Amp 5700 | high ROX | |
| Quantstudio™ 3 / 3 FAST | low Rox | |
| Quantstudio™ 5 / 5 FAST | low Rox | |
| Quantstudio™ 6 | low Rox | |
| Quantstudio™ 7 | low Rox | |
| Quantstudio™ 12 | low Rox | |
| QuantStudio™ 12K Flex system | low ROX | |
| Bioneer | Exicycler™96 | no ROX, optional |
| Exicycler™384 | no ROX, optional | |
| Biorad | CFX96™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | no ROX |
| CFX96 Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | no ROX | |
| CFX384 Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | no ROX | |
| CFX Opus 96 Real-Time PCR System | no ROX | |
| CFX Opus 384 Real-Time PCR System | no ROX | |
| CFX Connect™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | no ROX | |
| iQ5 Real-Time PCR Detection System | no ROX | |
| MiniOpticon™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | no ROX | |
| Opticon 2 – Continuous Fluorescence Detection System | no ROX | |
| Chromo4™ Four-Color Real-Time Detector | no ROX | |
| Bioron | RealLine Cycler 48-4 | no ROX, optional |
| RealLine Cycler 48-5 | no ROX, optional | |
| RealLine Cycler 96-4 | no ROX, optional | |
| RealLine Cycler 96-5 | no ROX, optional | |
| DNA Technology | Dtlite | no ROX, optional |
| Dtprime | no ROX, optional | |
| Eppendorf | Mastercycler® ep realplex 4, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | no ROX |
| Mastercycler® ep realplex 4s, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler® ep realplex, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler® ep realplex s, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler Nexus | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler Nexus gradient | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler Pro | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler Pro S | no ROX | |
| Mastercycler Pro 384 | no ROX | |
| Roche | LightCycler® 96 System | no ROX |
| LightCycler® 480 System | no ROX | |
| LightCycler® 2.0 Instrument | no ROX | |
| LightCycler® 1.5 Instrument | no ROX | |
| LightCycler® 1536 System | no ROX | |
| LightCycler® Nano System | no ROX | |
| Analytik Jena | qTower | low ROX (optional) |
| qTower 2.0 | low ROX (optional) | |
| qTower 2.2 | low ROX (optional) | |
| qTower 3 | low ROX (optional) | |
| qTower 3 84 | low ROX (optional) | |
| Stratagene / Agilent | AriaMx Real-time PCR System | no ROX |
| Mx3000P® qPCR System | low ROX | |
| Mx3005P® qPCR System | low ROX | |
| Mx4000® qPCR System | low ROX | |
| Qiagen | Rotor-Gene™ Q | low ROX |
| Rotor-Gene™ 6000 | low ROX | |
| Quantabio | Q | no ROX, optional |
qPCR in less than 20 minutes .
Extremely fast
The primaQUANT qPCR Master Mixes cope with the shortest cycle times due to their ultra fast DNA polymerase: a complete qPCR run takes less than 20 minutes under suitable conditions.
Of course, you can also use your previous qPCR protocol.
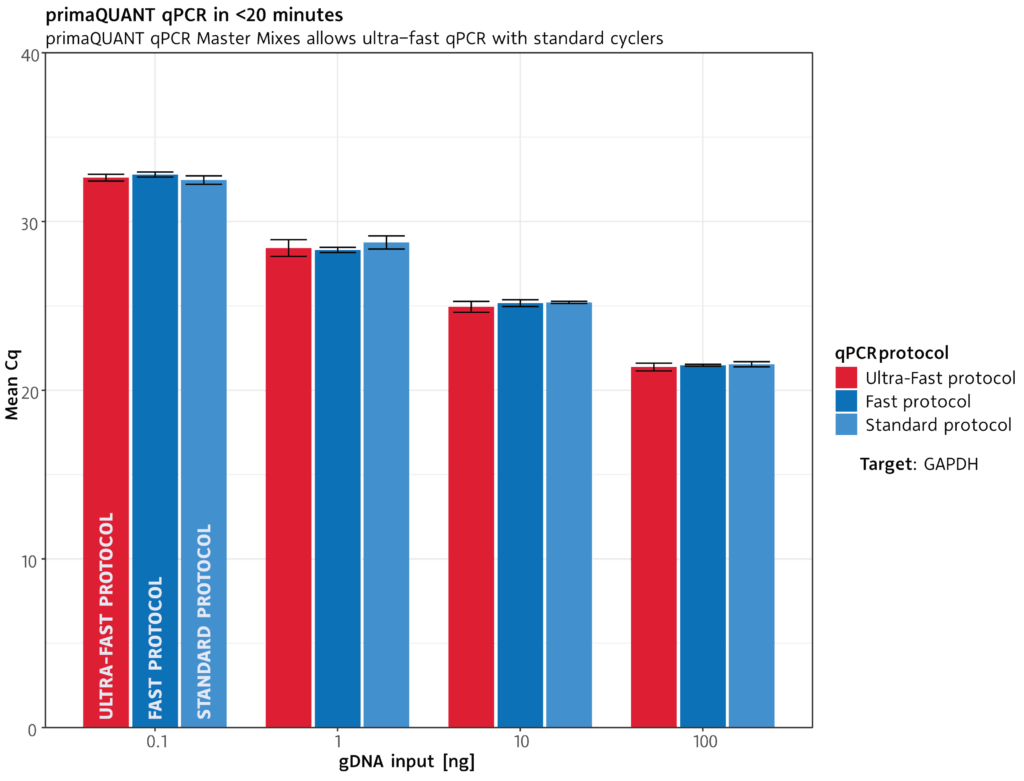
Standard protocol:
| Schritt | Zeit | Temperatur | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiale Denaturierung | 1-3 Minuten | 92°C – 95°C | |
| 25 – 40 Zyklen | Denaturierung | 5-10 Sekunden | 92°C – 95°C |
| Kombiniertes Annealing/Elongation | 10-20 Sekunden | 60°C – abhängig von den verwendeten Primern |
Fast protocol:
| Schritt | Zeit | Temperatur | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiale Denaturierung | 1 Minute | 92°C – 95°C | |
| 25 – 40 Zyklen | Denaturierung | 5 Sekunden | 92°C – 95°C |
| Kombiniertes Annealing/Elongation | 10 Sekunden | 60°C – abhängig von den verwendeten Primern |
Ultra Fast Protocol:
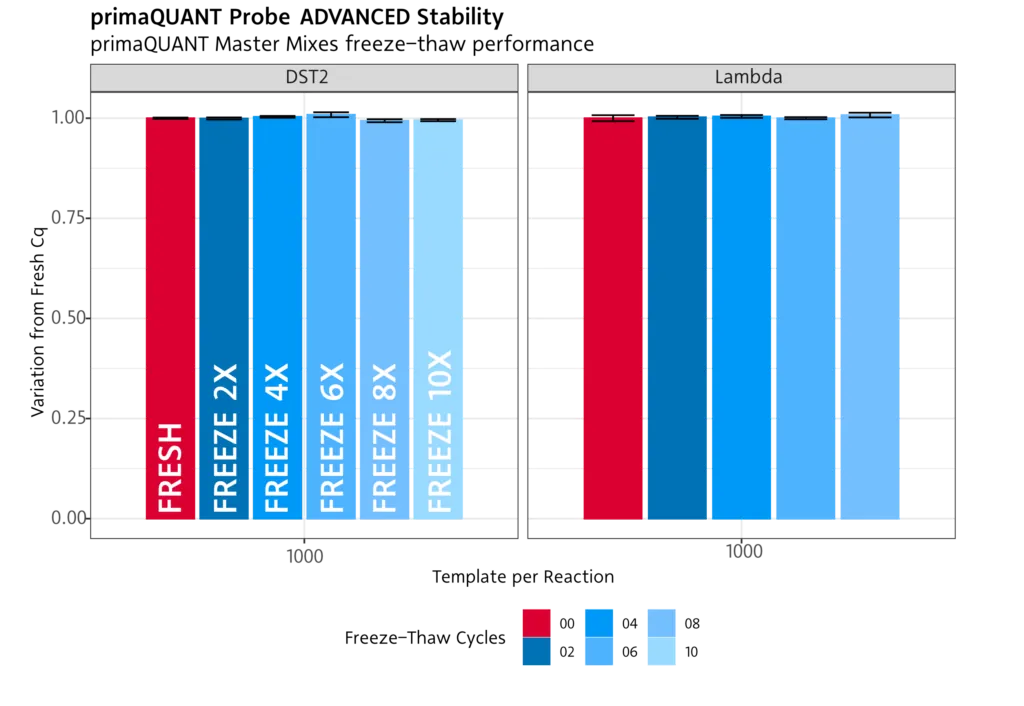
Temperature-stable .
Freeze/thaw
Our PCR and qPCR reagents are not affected by multiple freezing/thawing . You can therefore freeze and thaw the mixes more than 10 times without any problems.
Storage in the refrigerator
The primaQUANT Master Mixes are stable for weeks at 4°C. For short-term storage, we generally recommend storage at 4°C in the refrigerator.
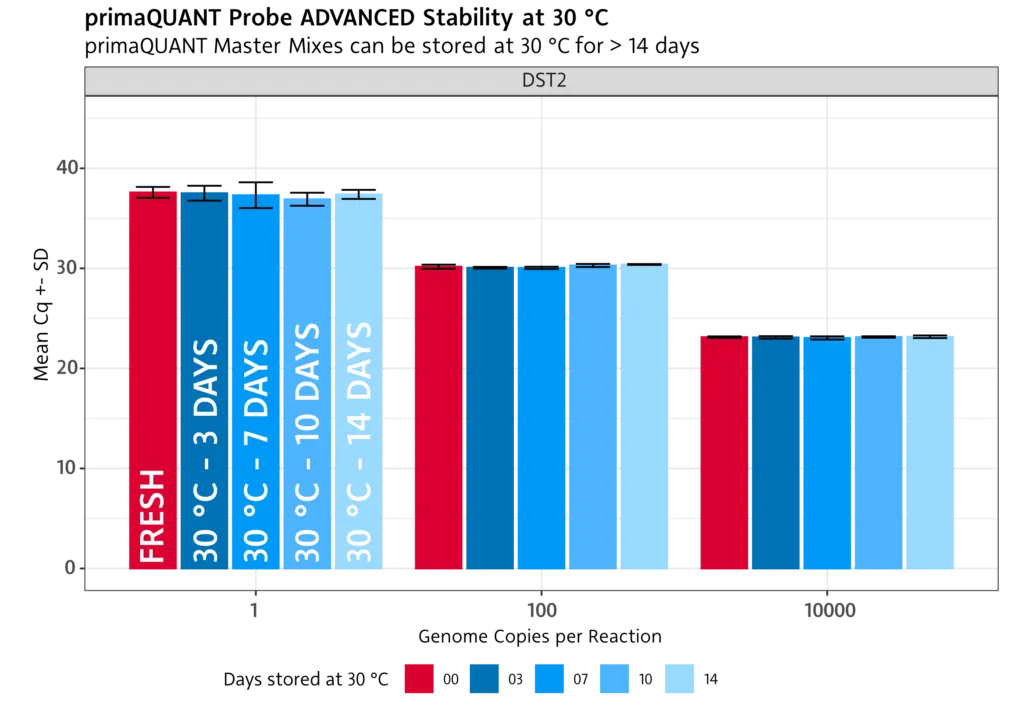
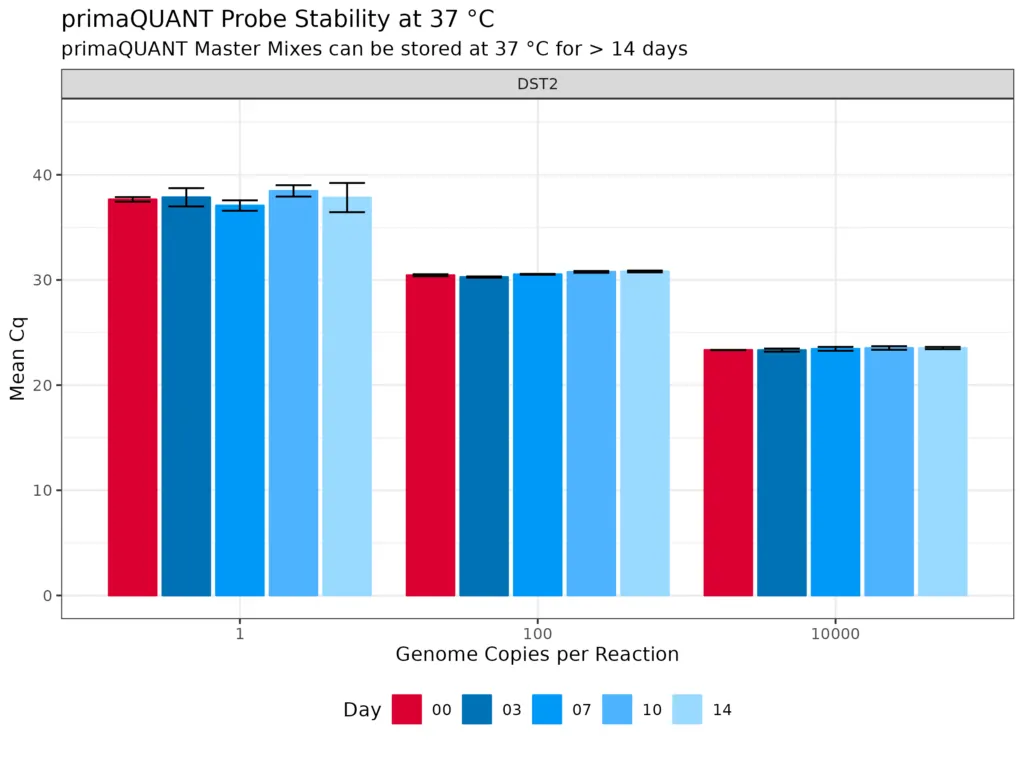
Stability at room temperature
The primaQUANT Master Mixes can even be stored for several days at room temperature without loosing quality. Therefore, you no longer have to pipette your qPCR laboriously on ice to avoid a loss of sensitivity!


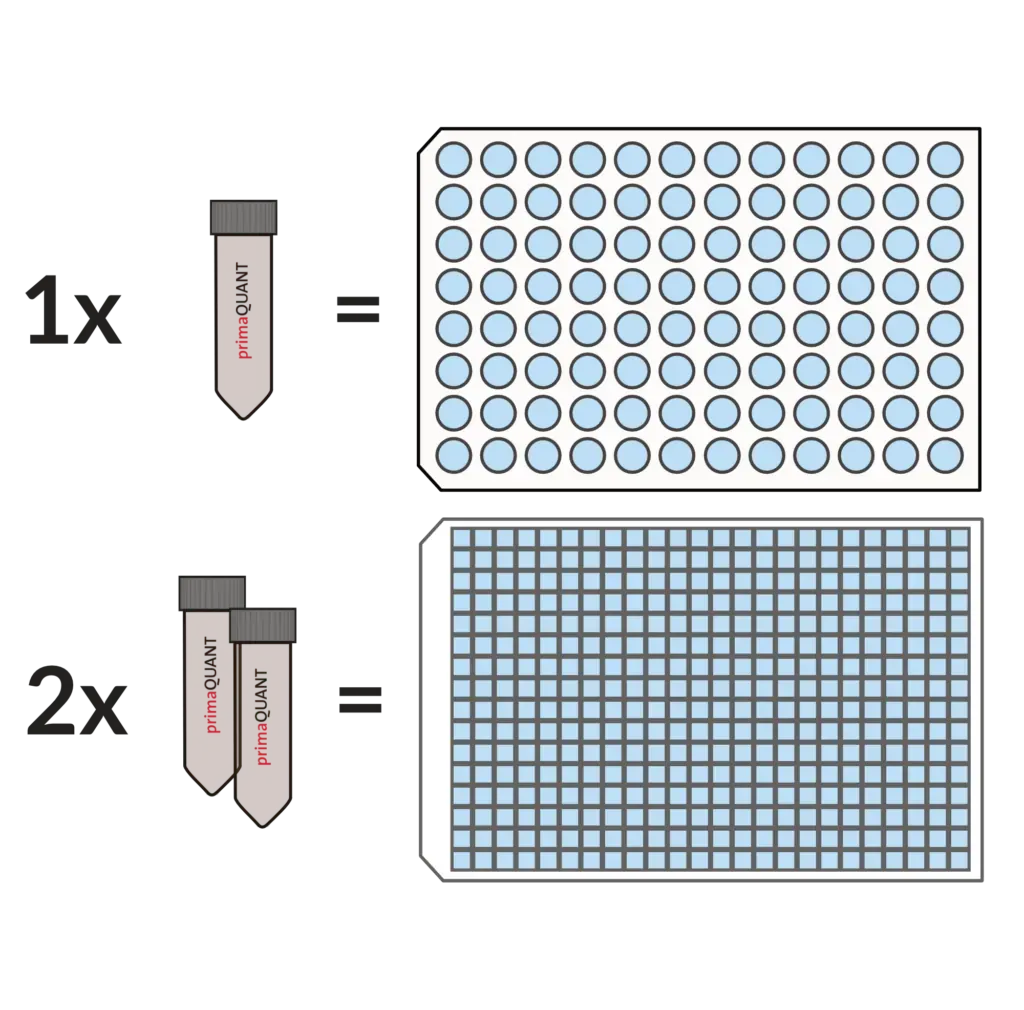
Smart Package Size .
No more annoying aliquoting!
Our Master Mixes come in units of 1 ml as standard.
This is very convenient and practical, because one tube is enough for exactly one 96 well plate, two tubes for one 384 well plate. If you ever need less, you can simply store the mixes in the refrigerator for several weeks.
Customized fillings: As the manufacturer, we can of course supply you with fillings and mixtures according to your special requirements.
Made in Germany .
We develop and produce our enzymes and master mixes exclusively ourselves in Germany. You benefit from this in several ways:
- Very short delivery times
- Fast and competent support
- ISO certified production
- High-end quality control
- Customized fillings or product adaptations

ADVANCED SYBR® Green Master Mixes .
Available with ROX or without ROX – suitable for all qPCR instruments.
Downloads and further information .
| Hersteller | qPCR Gerät | ROX notwendig? |
|---|---|---|
| Applied Biosystems / Thermo Fischer | StepOne™ Real-Time PCR System | Ja (high ROX) |
| StepOnePlus™ Real-Time PCR System | Ja (high ROX) | |
| 7500 Real-Time PCR System | Ja | |
| 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System | Ja | |
| 7500 Fast Dx Real-Time PCR Instrument | Ja | |
| 7500 Real-Time PCR System for Human Identification | Ja | |
| 7300 Real-Time PCR System | Ja (high ROX) | |
| Viia™ 7 Real-Time PCR System | Ja | |
| 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System | Ja (high ROX) | |
| OpenArray® Real-Time PCR Platform | Ja (high ROX) | |
| PRISM® 7000 Sequencing Detection System | Ja (high ROX) | |
| PRISM® 7700 Sequencing Detection System | Ja (high ROX) | |
| PRISM® 7900 Sequencing Detection System | Ja (high ROX) | |
| Gene Amp 5700 | Ja (high ROX) | |
| Quantstudio™ 3 / 3 FAST | Ja | |
| Quantstudio™ 5 / 5 FAST | Ja | |
| Quantstudio™ 6 | Ja | |
| Quantstudio™ 7 | Ja | |
| Quantstudio™ 12 | Ja | |
| QuantStudio™ 12K Flex system | Ja | |
| Bioneer | Exicycler™96 | Nein (optional) |
| Exicycler™384 | Nein (optional) | |
| Biorad | CFX96™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | Nein |
| CFX96 Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | Nein | |
| CFX384 Touch™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | Nein | |
| CFX Opus 96 Real-Time PCR System | Nein | |
| CFX Opus 384 Real-Time PCR System | Nein | |
| CFX Connect™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | Nein | |
| iQ5 Real-Time PCR Detection System | Nein | |
| MiniOpticon™ Real-Time PCR Detection System | Nein | |
| Opticon 2 – Continuous Fluorescence Detection System | Nein | |
| Chromo4™ Four-Color Real-Time Detector | Nein | |
| Bioron | RealLine Cycler 48-4 | Nein (optional) |
| RealLine Cycler 48-5 | Nein (optional) | |
| RealLine Cycler 96-4 | Nein (optional) | |
| RealLine Cycler 96-5 | Nein (optional) | |
| DNA Technology | Dtlite | Nein (optional) |
| Dtprime | Nein (optional) | |
| Eppendorf | Mastercycler® ep realplex 4, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | Nein |
| Mastercycler® ep realplex 4s, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | Nein | |
| Mastercycler® ep realplex, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | Nein | |
| Mastercycler® ep realplex s, Real-Time Thermal Cycler | Nein | |
| Mastercycler Nexus | Nein | |
| Mastercycler Nexus gradient | Nein | |
| Mastercycler Pro | Nein | |
| Mastercycler Pro S | Nein | |
| Mastercycler Pro 384 | Nein | |
| Roche | LightCycler® 96 System | Nein |
| LightCycler® 480 System | Nein | |
| LightCycler® 2.0 Instrument | Nein | |
| LightCycler® 1.5 Instrument | Nein | |
| LightCycler® 1536 System | Nein | |
| LightCycler® Nano System | Nein | |
| Analytik Jena | qTower | Ja |
| qTower 2.0 | Ja | |
| qTower 2.2 | Ja | |
| qTower 3 | Ja | |
| qTower 3 84 | Ja | |
| Stratagene / Agilent | AriaMx Real-time PCR System | Nein |
| Mx3000P® qPCR System | Ja | |
| Mx3005P® qPCR System | Ja | |
| Mx4000® qPCR System | Ja | |
| Qiagen | Rotor-Gene™ Q | Ja |
| Rotor-Gene™ 6000 | Ja | |
| Quantabio | Q | Nein (optional) |
Composition
| Komponente | Stock Konzentration | 20 µl Reaktion | 10 µl Reaktion | Finale Konzentration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| primaQUANT CYBR Master Mix | 2x | 10 µl | 5 µl | 1 x |
| Reverse Primer | 4 µM | 1 µl | 0,5 µl | 200 nM (100 – 400 nM empfohlen) |
| Forward Primer | 4 µM | 1 µl | 0,5 µl | 200 nM (100 – 400 nM empfohlen) |
| Template (DNA/cDNA) | – | variabel | variabel | 0,1 – 10 ng/Reaktion |
| Steriles Wasser | – | auf 20 µl | auf 10 µl | – |
Standard protocol
3-Step
| Schritt | Zeit | Temperatur | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiale Denaturierung | 1-3 Minuten | 92°C – 95°C | |
| 25 – 40 Zyklen | Denaturierung | 5-10 Sekunden | 92°C – 95°C |
| Annealing | 1-5 Sekunden | 60°C – abhängig von den verwendeten Primern | |
| Extension | 10-20 Sekunden | 72°C |
2-Step
| Schritt | Zeit | Temperatur | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiale Denaturierung | 1-3 Minuten | 92°C – 95°C | |
| 25 – 40 Zyklen | Denaturierung | 5-10 Sekunden | 92°C – 95°C |
| Kombiniertes Annealing/Elongation | 10-20 Sekunden | 60°C – abhängig von den verwendeten Primern |
Ultra-FAST protocol
3-Step
| Schritt | Zeit | Temperatur | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiale Denaturierung | 1 Minute | 92°C – 95°C | |
| 25 – 40 Zyklen | Denaturierung | 1-5 Sekunden | 92°C – 95°C |
| Annealing | 1-5 Sekunden | 60°C – abhängig von den verwendeten Primern | |
| Extension | 1 Sekunde | 72°C |
2-Step
Master mix calculation
| Name of PCR | |||
| Number of Reactions | 10 | ||
| Final Volume per Reaction | 20 | ul | |
| Reagents | Stock Concentration | Final Concentration | Volume to add [µl] |
| qPCR Master Mix [x-times concentrated] | 2 | 1 | 100 |
| Reverse Primer [µM] | 10 | 0.3 | 6 |
| Foward Primer [µM] | 10 | 0.3 | 6 |
| PCR-grade Water | 87 | ||
| Total Volume per reaction (without template) [µl] | 19.9 | ||
| Total Volume of Final Master Mix (without template) [µl] | 199 | ||
| cDNA/DNA Template | Volume within reaction [µl] | ||
| Stock Concentration | 100 | [ng/µl] | |
| Desired amount per well | 10 | ng per reaction | 0.1 |
| Aliquot | 1.9900 | µl per well of Final Master Mix | |
| add | 0.1 | µl per well of DNA/cDNA Template | |



