
NGS and PCR cleanup .
Magnetic beads are very efficient for the purification of PCR products and size selection of amplicons in sequencing.
Our MagSi-NGSPREP Plus beads are comptible with most established NGS protocols, e.g. Ampure XP .
MagSi-DT Removal Beads remove dye terminators and unincorporated dyes from sequencing reactions – without centrifugation or filtration.
Hard Facts .
- Compatible with existing protocols
- High purity and recovery
- Easily scalable and HTS compatible
- MagSi DT-Removal: removal of impurities such as dye terminators
- MagSi-NGSPREPplus: SPRI-based size selection
- Guarantee consistent and robust results

Applications .
Library preparation is one of the most important steps in sample preparation for NGS reactions. MagSi NGS beads allow easy size selection by varying the bead : sample ratio.
The MagSi-NGSPREP Plus beads are also suitable for size selection of your PCR products (SPRI).
By varying the bead-to-sample ratio, you can select desired fragment sizes or remove unwanted fragment sizes.
With MagSi-NGSPREP Plus Beads you can remove enzymes, primers, oligonucleotides, as well as polymerases and salts easily and quickly from your PCR product.
Removal of unincorporated dyes and salts after sequencing reactions with our MagSi-DT Removal Beads.
With an adapted protocol, MagSi-NGSPREP Plus beads can also be used to enrich RNA to improve the sensitivity and specificity of reverse transcription and qPCR analysis.
Simon, B., Pichon, M., Valette, M., Burfin, G., Richard, M., Lina, B., & Josset, L. (2019). Whole Genome Sequencing of A(H3N2) Influenza Viruses Reveals Variants Associated with Severity during the 2016-2017 Season. Viruses, 11(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020108
Details .
Easy-to-use .
- MagSi-NGSPREP: One product for all cleanup and size selection steps in the library preparation workflow
- Uncomplicated protocol with bind-wash-elute method
- For manual and automated workflows
MagSi-NGSPREP Plus .
Our MagSi-NGSPREP Plus beads are very efficient in NGS applications, both for size selection and library prep clean-up.
- Excellent purification of PCR products
- Efficient removal of enzymes, primers, oligonucleotides, polymerases and other contaminants
- Guaranteed consistent sequencing results
- Protocol identical to Agencourt AMPure XP®.
- Easy to automate, suitable for HTS
- Optimized protocols for liquid handlers available (Biomek®, Hamilton® Microlab STAR)
- Also suitable for liquid handlers from PerkinElmer®, Agilent Technologies® and others.
- Best performance in combination with our magnetic devices for 96 and 384 well plates.
| Item number | Product | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| MDKT00010005 | MagSi-NGSPREP Plus | 5 ml |
| MDKT00010075 | MagSi-NGSPREP Plus | 75 ml |
| MDKT00010500 | MagSi-NGSPREP Plus | 500 ml |
MagSi-NGSPREP Beads for best results .
- High recovery
- Fragment size selection adjustable between 100 and 1000 base pairs
- Guaranteed consistent sequencing results
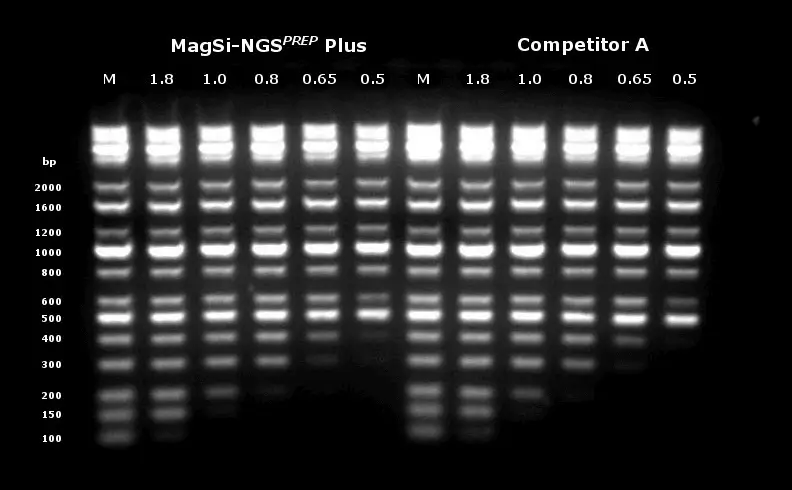
Size selection of a DNA ladder using different bead to sample ratios (0.5x to 1.8x). Top on agarose gel, bottom with bioanalyzer measurements.
Source: magtivio
MagSi-DT Removal Beads .
MagSi-DT removal beads are very efficient in removing dye terminators from BigDye® sequencing reactions.
- High signal intensity and Phred 20 read length
- Efficient removal of unincorporated dye terminators and salts
- Consistent and robust performance
- Easy automation, HTS compatible
- No centrifugation or filtration steps necessary
- Purification directely in the reaction plates
- Protocol identical to Agencourt CleanSEQ®.
- Optimized for Biomek® Workstations and Hamilton® Microlab STARline
- Compatible with many other automated liquid handling systems (e.g. PerkinElmer®, Caliper Life Sciences®, etc.)
| Item number | Product | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| MDKT00040008 | MagSi-DT Removal | 8 ml |
| MDKT00040050 | MagSi-DT Removal | 50 ml |
| MDKT00040500 | MagSi-DT Removal | 500 ml |
MagSi-DT Removal Beads for best results .
The MagSi-DT Removal Beads are very efficient in removing dye terminators from BigDye® sequencing reactions.
- Efficient removal of unincorporated dye terminators and salts.
- High signal intensities and long Phred 20 read lengths
- High pass rates
- Consistent performance

NGS and DT Removal Beads .
Downloads .
Simon, B., Pichon, M., Valette, M., Burfin, G., Richard, M., Lina, B., & Josset, L. (2019). Whole Genome Sequencing of A(H3N2) Influenza Viruses Reveals Variants Associated with Severity during the 2016-2017 Season. Viruses, 11(2), 108. https://doi.org/10.3390/v11020108
Recovery of Methanotrophic Activity Is Not Reflected in the Methane-Driven Interaction Network after Peat Mining | Applied and Environmental Microbiology
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Multi-omics integration identifies a selective vulnerability of colorectal cancer subtypes to YM155 – Zhan – 2021 – International Journal of Cancer – Wiley Online Library
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Pathogens | Free Full-Text | Microeukaryotic Communities on the Fruit of Gardenia thunbergia Thunb. with a Focus on Pathogenic Fungi. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
When the going gets tough: Emergence of a complex methane-driven interaction network during recovery from desiccation-rewetting – ScienceDirect
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Association between childhood maltreatment, psychopathology and DNA methylation of genes involved in stress regulation: Evidence from a study in Borderline Personality Disorder
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Impact of PNPase on the transcriptome of Rhodobacter sphaeroides and its cooperation with RNase III and RNase E | SpringerLink
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Ammonium Removal in Aquaponics Indicates Participation of Comammox Nitrospira | SpringerLink
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Active metabolic pathways of anaerobic methane oxidation in paddy soils – ScienceDirect
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Limited antimicrobial efficacy of oral care antiseptics in microcosm biofilms and phenotypic adaptation of bacteria upon repeated exposure | SpringerLink
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Monitoring and contamination incidence of gnotobiotic experiments performed in microisolator cages – ScienceDirect
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Metagenomic Analysis of Bacterial Communities in Agricultural Soils from Vietnam with Special Attention to Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Forests | Free Full-Text | Impact of Soil-Applied Microbial Inoculant and Fertilizer on Fungal and Bacterial Communities in the Rhizosphere of Robinia sp. and Populus sp. Plantations. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Induced systemic resistance impacts the phyllosphere microbiome through plant-microbe-microbe interactions | bioRxiv
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Allergies | Free Full-Text | Could Modifying the Skin Microbiome, Diet, and Lifestyle Help with the Adverse Skin Effects after Stopping Long-Term Topical Steroid Use? (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Structure-based analyses of Salmonella RcsB variants unravel new features of the Rcs regulon | Nucleic Acids Research | Oxford Academic
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Life | Free Full-Text | The Effect of a Total Fishmeal Replacement by Arthrospira platensis on the Microbiome of African Catfish (Clarias gariepinus)
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Densely Populated Water Droplets in Heavy-Oil Seeps | Applied and Environmental Microbiology
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Early Stage Root-Associated Fungi Show a High Temporal Turnover, but Are Independent of Beech Progeny
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Pulmonary microbiome patterns correlate with the course of disease in patients with sepsis-induced ARDS following major abdominal surgery – Journal of Hospital Infection
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Frontiers | Novel Antimicrobial Cellulose Fleece Inhibits Growth of Human-Derived Biofilm-Forming Staphylococci During the SIRIUS19 Simulated Space Mission | Microbiology
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Microorganisms | Free Full-Text | Staphylococcus saccharolyticus: An Overlooked Human Skin Colonizer
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Frontiers | Targeted De-Methylation of the FOXP3-TSDR Is Sufficient to Induce Physiological FOXP3 Expression but Not a Functional Treg Phenotype | Immunology
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
PD-1 (PDCD1) promoter methylation in Merkel cell carcinoma: prognostic relevance and relationship with clinico-pathological parameters | Modern Pathology
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Targeted bisulfite sequencing: A novel tool for the assessment of DNA methylation with high sensitivity and increased coverage – PubMed
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Transcriptional mutagenesis dramatically alters genome-wide p53 transactivation landscape – PubMed
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Global discovery of bacterial RNA-binding proteins by RNase-sensitive gradient profiles reports a new FinO domain protein – PubMed
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
BG – Authigenic formation of Ca-Mg carbonates in the shallow alkaline Lake Neusiedl, Austria
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
An RNA-centric global view of Clostridioides difficile reveals broad activity of Hfq in a clinically important Gram-positive bacterium | bioRxiv
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Prevalence of p53 dysregulations in feline oral squamous cell carcinoma and non-neoplastic oral mucosa – PubMed.
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022
Land Use Change and Water Quality Use for Irrigation Alters Drylands Soil Fungal Community in the Mezquital Valley, Mexico – PubMed.
. (n.d.). Retrieved April 5, 2022

