
Protein purification .
Magnetic beads are ideal for purification and isolation of proteins and peptides for bioassays, mass spectrometry, SDS-PAGE, immunoassays and biomarker analysis.
MagSi Protein A and Protein G beads bind the Fc region of antibodies and can be used for immunoprecipitation or immunoassays.
MagSi-S proteomics beads with C4, C8, or C18 surface modification enable the purification or desalting of large biomolecules such as proteins as well as smaller peptides.
MagSi-WCX and MagSi-WAX can be used for the enrichment and desalting of proteins and peptides.
Hard Facts .
- Fast and easy protein purification
- High purity and yield
- Wide range of applications
- Different coatings available
- Alkyl radicals (C4-C18) for reverse phase applications
- Weak Cation / Anion Exchange (WCX / WAX) available
Applications .
MagSi beads are suitable for sample preparation for analyses such as MALDI-TOF. Low molecular weight peptides from plasma or urine can be concentrated and used directly in MS after elution.
Hussien, A. K., Moez, P. E., Elwakil, H. S., & Elagaan, H. A. (2020). Identification of urinary proteomic profile of patients with chronic allograft nephropathy. Alexandria Journal of Medicine, 56(1), 93-104. https://doi.org/10.1080/20905068.2020.1749782
Rizk, M. M., Sharaki, O. A., Meleis, M. E., Younan, D. N., Elkial, A. A., & Moez, P. (2019). Detection of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer using C8Magnetic Bead Separation and MALDI-TOF Plasma Proteome Profiling in Egyptian Females. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 20(12), 3603-3609. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.12.3603
Purification of a wide variety of proteins for size analysis on SDS-PAGEs.
Separation of peptides and proteins for downstream applications.
Removal of detergents from protein and peptide solutions.
Enrichment of phosphorylated proteins and peptides with the MagSi-WCX beads.
Biomarker analyses can be supported by proteome purification via magnetic beads.
Rizk, M. M., Sharaki, O. A., Meleis, M. E., Younan, D. N., Elkial, A. A., & Moez, P. (2019). Detection of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer using C8Magnetic Bead Separation and MALDI-TOF Plasma Proteome Profiling in Egyptian Females. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 20(12), 3603-3609. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.12.3603
Antigens can be precipitated by incubation with specific antibodies. These immunoprecipitates can be fished from the samples by beads containing covalently bound protein A or protein G.
Hjeij, R., et al. (2014). CCDC151 Mutations Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia by Disruption of the Outer Dynein Arm Docking Complex Formation. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 95(3), 257-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.08.005
Magentic beads with covalently bound protein A or protein G are excellent for binding and purification of IgG antibodies from samples.
Details .
Product overview protein and peptide purification .
| Surface modification | Concentration | Target molecule | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MagSi-Protein A | Protein A | 10 mg/ml | Immunoglobulin (Fc region) |
| MagSi-Protein G | Protein G | 10 mg/ml | Immunoglobulin (Fc region) |
| MagSi-proteomics | Alkyl chains | 10 mg/ml | Peptides and proteins |
| MagSi-WCX | Weak Cation Exchange Surface | 20 mg/ml | Proteins with positive net charge |
| MagSi-WAX | Weak Anion Exchange Surface | 20 mg/ml | Proteins with negative net charge |
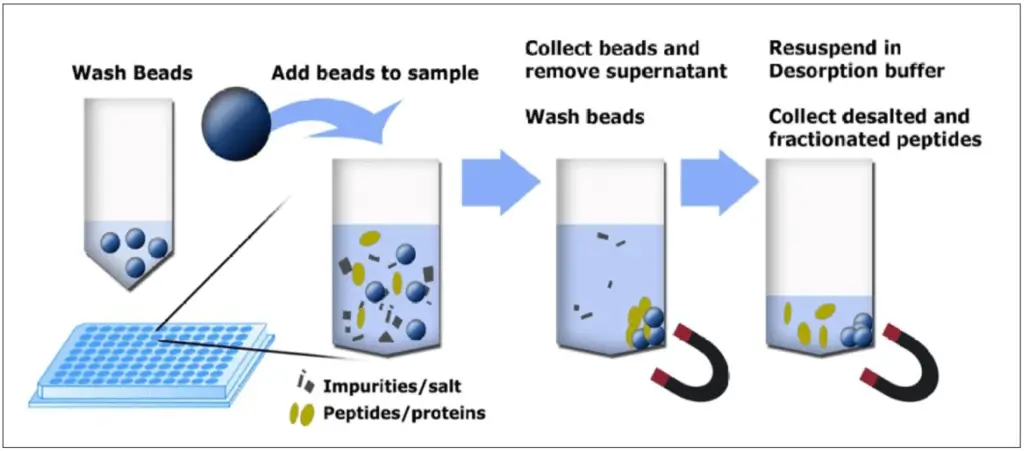
Simple workflow for protein purification .
Magnetic beads with weak anion exchange (WAX), weak cation exchange (WCX) or C-chains (C8, C14 or C18) on the surface allow straightforward protein purification.
MagSi Protein A Beads .
Magnetic beads with covalently bound recombinant protein A for antibody purification and immunoassays.
- Efficient binding of the Fc region of immunoglobulins.
- Simple immobilization of various biomolecules
- Different types and particle sizes, ideal for immunoprecipitation (IP) and IgG purification
- Also suitable for HTS due to simple automation
- 3 sizes available: 600 nm, 1000 nm or 3000 nm diameter
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD10011 | 1 ml | MagSi-protein A 600 | 10 mg/ml | 600 nm |
| MD11011 | 5 ml | |||
| MD01011 | 1 ml | MagSi-protein A 1.0 | 10 mg/ml | 1.0 µm |
| MD02011 | 5 ml | |||
| MD41011 | 1 ml | MagSi-protein A 3.0 | 10 mg/ml | 3.0 µm |
| MD42011 | 5 ml |
Binding strength to protein A .
| Species | Antibody class | Protein A binding |
|---|---|---|
| Human | Total IgG | ++++ |
| IgG1 | + | |
| IgG2 | ++++ | |
| IgG3 | ++++ | |
| IgG4 | ++++ | |
| Mouse | Total IgG | ++++ |
| IgG1 | + | |
| IgG2A | ++++ | |
| IgG2B | ++++ | |
| IgG3 | +++ | |
| Rat | Total IgG | + |
| IgG1 | – | |
| IgG2A | – | |
| IgG2B | – | |
| IgG2C | ++ | |
| Hamster | Total IgG | ++ |
| Guinea pig | Total IgG | ++++ |
| Rabbit | Total IgG | ++++ |
| Horse | Total IgG | ++ |
| Cow | Total IgG | ++ |
| Pig | Total IgG | +++ |
| Sheep | Total IgG | + |
| Goat | Total IgG | + |
| Chicken | Total IgG | – |
MagSi Protein G Beads .
Magnetic beads with covalently bound protein G for antibody purification and immunoassays
- Recombinant protein G covalently bound to the bead surface
- Efficient binding of the Fc region of immunoglobulins.
- Suitable for immobilization of different biomolecules
- Different particle sizes, ideal for immunoprecipitation (IP) and IgG purification
- Suitable for HTS due to simple automation capability
- 3 bead sizes available: 600 nm, 1000 nm or 3000 nm diameter
| Item number | Volume | Product | Concentration | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD10012 | 1 ml | MagSi-protein G 600 | 10 mg/ml | 600 nm |
| MD11012 | 5 ml | |||
| MD01012 | 1 ml | MagSi-protein G 1.0 | 10 mg/ml | 1.0 µm |
| MD02012 | 5 ml | |||
| MD41012 | 1 ml | MagSi-protein G 3.0 | 10 mg/ml | 3.0 µm |
| MD42012 | 5 ml |
Binding strength to protein G .
| Species | Antibody class | Protein G binding |
|---|---|---|
| Human | Total IgG | ++++ |
| IgG1 | ++++ | |
| IgG2 | ++++ | |
| IgG3 | ++++ | |
| IgG4 | ++++ | |
| Mouse | Total IgG | ++++ |
| IgG1 | +++ | |
| IgG2A | ++++ | |
| IgG2B | ++++ | |
| IgG3 | +++ | |
| Rat | Total IgG | ++ |
| IgG1 | + | |
| IgG2A | ++++ | |
| IgG2B | ++ | |
| IgG2C | +++ | |
| Hamster | Total IgG | ++ |
| Guinea pig | Total IgG | ++ |
| Rabbit | Total IgG | +++ |
| Horse | Total IgG | ++++ |
| Cow | Total IgG | ++++ |
| Pig | Total IgG | ++ |
| Sheep | Total IgG | ++ |
| Goat | Total IgG | ++ |
| Chicken | Total IgG | – |
MagSi-proteomics Beads .
MagSi-S proteomics beads are optimized for purification, concentration or desalting of peptides and protein fragments. The surface of MagSi proteomics beads is modified by covalently bonded C4, C8 or C18 alkyl groups and is therefore very well suited for reverse phase applications.
MagSi-S proteomics C4: suitable for capture, concentration and purification of proteins from protein mixtures, cell lysates, culture supernatant (e.g. secreted proteins).
MagSi-S proteomics C8: suitable for the capture and purification of peptides and proteins from clinical samples such as urine, saliva and cerebrospinal fluid.
MagSi-S proteomics C18: suitable for desalting of peptides or trypsin protein digestion prior to mass spectrometry, concentration of peptides (e.g. secreted peptides), capture and purification of peptides and proteins from serum and plasma.
- Beads for purification, concentration and desalting of peptides or protein digestion
- Also suitable for sample preparation before mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
- Surface-bound alkyl groups (C4, C8 or C18) for reverse phase applications
- Easy to automate and suitable for HTS
| Item number | Product | Surface modification | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| MD01014 | MagSi-S proteomics C4 | C4 alkyl group | 2 ml |
| MD02014 | 10 ml | ||
| MD03014 | 100 ml | ||
| MD01015 | MagSi-S proteomics C8 | C8 alkyl group | 2 ml |
| MD02015 | 10 ml | ||
| MD03015 | 100 ml | ||
| MD01009 | MagSi-S proteomics C18 | C18 alkyl group | 2 ml |
| MD03009 | 10 ml | ||
| MD04009 | 100 ml |
MagSi-WCX (weak cation exchange) Beads .
Magnetic silica particles with weak cation exchange surface (WCX). MagSi-WCX is ideal for reducing the complexity of proteins or peptides. Applications include sample preparation and pre-fractionation prior to mass spectrometry or SDS-PAGE analysis, biomarker analysis, and serum/plasma profiling.
| Item number | Product | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| MD01023 | MagSi-WCX | 2 ml |
| MD02023 | 10 ml | |
| MD03023 | 100 ml |
MagSi-WAX (weak anoin exchange) Beads .
Magnetic silica particles with weak anion exchange surface (WAX). MagSi-WAX is ideal for reducing the complexity of proteins or peptides. Applications include sample preparation and pre-fractionation prior to mass spectrometry or SDS-PAGE analysis, biomarker analysis, and serum/plasma profiling.
| Item number | Product | Volume |
|---|---|---|
| MD01025 | MagSi-WAX | 2 ml |
| MD02025 | 10 ml | |
| MD03025 | 100 ml |
Magnetic beads for protein purification .
Magentic beads available with different surfaces: Protein A or G coupling, alkyl residues as well as WCX or WAX beads.
Downloads .
Hjeij, R., et al. (2014). CCDC151 Mutations Cause Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia by Disruption of the Outer Dynein Arm Docking Complex Formation. The American Journal of Human Genetics, 95(3), 257-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.08.005
Hussien, A. K., Moez, P. E., Elwakil, H. S., & Elagaan, H. A. (2020). Identification of urinary proteomic profile of patients with chronic allograft nephropathy. Alexandria Journal of Medicine, 56(1), 93-104. https://doi.org/10.1080/20905068.2020.1749782
Rizk, M. M., Sharaki, O. A., Meleis, M. E., Younan, D. N., Elkial, A. A., & Moez, P. (2019). Detection of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer using C8Magnetic Bead Separation and MALDI-TOF Plasma Proteome Profiling in Egyptian Females. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 20(12), 3603-3609. https://doi.org/10.31557/APJCP.2019.20.12.3603

